Maximize Efficiency: Integrating Cloud Computing into Your Operational Stack
Table of Contents
Why cloud computing?
In our world today, the technological landscape may be likened to that of a mythological multi-headed dragon – Menacing, fierce and rapidly evolving. This evolution has led to a great burst of progress in the tech and business world, especially in regards to security.
In the past/present, most businesses made use of physical servers and physical storage devices to manage data and while this method served its purpose, a much better alternative would appear in the form cloud services (security, protection from insults i.e a fire and unlimited storage space makes choosing this method of storage a no-brainer ). Cloud computing offers these advantages and it has become a cornerstone for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. By integrating cloud computing into operational stacks, organizations can leverage a multitude of benefits that drive innovation and competitive advantage.
This article explores the significance of cloud computing in modern operational stacks, the various cloud services available, and real-world examples of successful implementation.
What is Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). This model allows businesses to access and manage resources on demand, without the need for owning and maintaining physical hardware.
In short, cloud computing is simply a way to access data and services on the internet instead of on one device i.e your computer. You can use the cloud to assess these services from virtually anywhere in the world and from any device too. You may be on a flight to South Africa, on a bus to work or even on vacation in Hawaii and you would be able to access the same document you were reading or working on your laptop, phone, etc because it’s all online.
A simple example of cloud computing in everyday life would be using Google Drive to store your pictures, iCloud for the same, google docs for your documents, etc.
Who uses cloud computing?
Everyone! Everyone uses cloud computing most times without realizing it. Our phones, smartwatches, laptops have been configured to store important information on the cloud. More importantly, cloud computing is particularly effective for businesses. Cloud computing has been adopted by enterprises of all sizes and across all industries because it provides them with flexibility and scalability. Data security, software development, data analytics, disaster recovery, virtual desktops, server virtualization, and customer-facing apps are among the common tasks for which businesses employ it.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Scalability: Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their operations up or down based on demand. This flexibility is crucial for handling varying workloads and ensuring optimal performance during peak times.
2. Cost Efficiency: By utilizing cloud services, organizations can reduce the capital expenditure associated with purchasing and maintaining hardware. Instead, they can opt for a pay-as-you-go model, paying only for the resources they use.
3. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud solutions offer great disaster recovery options, ensuring that data is backed up and can be quickly restored in the event of a system failure, a fire, or cyberattack.
4. Collaboration and Remote Work: Cloud computing facilitates seamless collaboration among teams, regardless of their physical location. This is particularly relevant in the current era of remote work.
5. Innovation and Agility: Cloud platforms provide access to cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics, enabling businesses to innovate and respond swiftly to market changes.
So, by what mechanism does Cloud computing really work?
To be succinct, cloud computing consists of three main components:
- Cloud service providers keep their apps and data on real computers in places called data centers. Examples of such cloud service providers include: Google cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure, etc.
- They provide users with access to those resources.
- Instantaneously, the internet connects users and providers over great distances.
The technology that connects the seemingly basic parts is intricate. To understand it, think about how things operated prior to the cloud: IT departments of businesses oversaw their own on-site data centers, which necessitated frequent hardware upgrades, astronomical energy costs, and copious quantities of space. It was costly, unworkable, and ineffective.
However, that is no longer required. Businesses who previously managed their own data centers are free from the concerns of deploying, securing, scaling, maintenance, and modernization. They don’t worry about the technological details; instead, they just concentrate on creating amazing consumer experiences. This fundamentally alters and streamlines how companies handle their IT resources.
Subscription-based services are provided by numerous cloud providers, for instance. Customers can get all the computer power they require for a monthly price. This eliminates the need for them to purchase software licenses, replace aging servers, purchase additional hardware when storage runs low, or install software upgrades to stay up to date with changing security risks. That is all taken care of by the vendor.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are different types of clouds knowing them will help you make informed choices about which one will work best for your company.
The three main types of Cloud Computing are Public cloud, Private cloud and Hybrid cloud. Within these deployment models, there are four main services: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
- Public cloud:
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud providers for public use. They own all of the cloud’s infrastructure, software, and hardware. The apps and data stored in the cloud are owned by their clients.
- Private cloud:
Organizations of any size, from businesses to academic institutions, can host private clouds—also referred to as internal, corporate, or on-premise clouds—for their own exclusive usage. When they do, they host the cloud on-site or remotely and own the underlying infrastructure.
- Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid clouds combine the greatest aspects of both public and private clouds. For sensitive or important tasks, businesses typically utilize private clouds; for spikes in computing demand, they use public clouds. Applications and data frequently move across them automatically. This increases organizational flexibility without forcing them to renounce their current security, compliance, and infrastructure.
N.B When a user utilizes a hybrid cloud from different suppliers i.e. A business owner may choose a hybrid cloud setup – Private on Microsoft Azure and Public on Google Cloud Platform (GCP), this mode of execution is known as a Multi cloud.
Integrating Cloud Computing into Operational Stacks
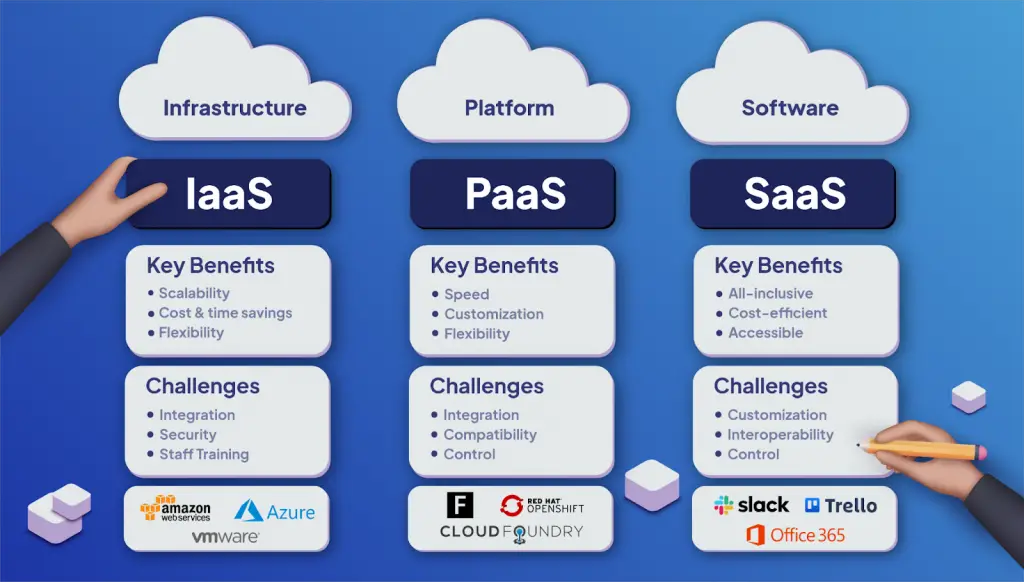
Integrating cloud computing into this stack involves several key components known as the cloud service models. These include :
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Software as a service (SaaS)
Cloud Service Providers
Leading Cloud service providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):

AWS offers a wide range of services, including EC2 for virtual servers, S3 for storage, and RDS for managed databases. AWS’s global infrastructure ensures low latency and high availability.
- Microsoft Azure:
Azure provides a comprehensive suite of IaaS offerings, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. Its integration with Microsoft products and services makes it a popular choice for enterprises.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP offers scalable and reliable IaaS solutions, including Compute Engine for virtual machines and Cloud Storage for object storage. GCP’s strengths lie in its data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- Google App Engine:

Part of GCP, App Engine enables developers to build scalable web and mobile applications. It automatically manages infrastructure concerns such as scaling and load balancing.
- Heroku:

Known for its simplicity and developer-friendly environment, Heroku supports multiple programming languages and offers easy deployment and scaling of applications.
- Microsoft Azure App Service:
This PaaS offering supports various programming languages and frameworks, providing integrated tools for development, deployment, and monitoring.
- Salesforce:

A leading CRM platform, Salesforce offers a suite of cloud-based applications for sales, service, marketing, and more. It enables businesses to manage customer relationships and drive sales growth.
Cloud Integration in Action: Case Studies from Leading Businesses
- Netflix
Netflix, the global streaming giant, leverages AWS (Amazon Web Service) to power its video streaming service. By using AWS’s vast infrastructure, Netflix can dynamically scale its resources to handle millions of concurrent viewers. AWS also provides robust data analytics capabilities, helping Netflix personalize content recommendations and improve user experience.
- Airbnb
Airbnb, the popular home-sharing platform, utilizes a combination of AWS and GCP to manage its global operations. These cloud services enable Airbnb to scale its infrastructure, process large volumes of data, and ensure high availability and reliability for its users.
- Spotify
Spotify, the music streaming service, relies on GCP for its data processing and analytics needs. GCP’s data analytics tools, such as BigQuery, help Spotify analyze user behavior and deliver personalized music recommendations.
In conclusion, Integrating cloud computing into modern operational stacks is essential for businesses looking to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. By leveraging IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions, organizations can achieve scalability, cost efficiency, and innovation. Real-world examples from companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and Spotify demonstrate the transformative impact of cloud computing. As businesses continue to embrace cloud technologies, they can unlock new opportunities for growth and success.
References
1. “The Basics of Cloud Computing” – Amazon Web Services. [AWS Cloud Computing] What is Cloud Computing? – Cloud Computing Services, Benefits, and Types – AWS
2. “What is Microsoft Azure?” – Microsoft Azure. [Azure Overview] What is Azure—Microsoft Cloud Services
3. “Google Cloud Platform” – Google Cloud. [GCP Overview] GCP overview
4. “Salesforce Overview” – Salesforce. [Salesforce Cloud] What is Salesforce? | What does Salesforce do? – Salesforce.com US
5. “The Power of Google Workspace” – Google. [Google Workspace] Google Workspace
6. “Netflix and AWS” – Amazon Web Services Case Studies. [Netflix Case Study] AWS Innovator: Netflix | Case Studies, Videos and Customer Stories
7. “Airbnb Leverages AWS and GCP” – Various Sources. Airbnb cloud strategy
8. “Spotify and Google Cloud Platform” – Google Cloud. [Spotify Case Study] Spotify Case Study | Google Cloud